Long Call
Long call: buyers of call options hope the stock price to increase substantially. In this case the subsequent selling the call before the expiration will result in profit for the buyer.
The loss is limited to the option premium the buyer paid for its purchase. The buyer loses his money if the spot price of the particular asset is less than the strike price when expiring.
Long calls establish limited risk and unlimited reward. The break-even point of this kind of option is equal to strike price plus premium. Long calls are used when the buyers are bullish on the market. Call options can be either American or European contracts. Call option buyers should pay attention to the intrinsic value of the option and its time value in order to pay less for the time.
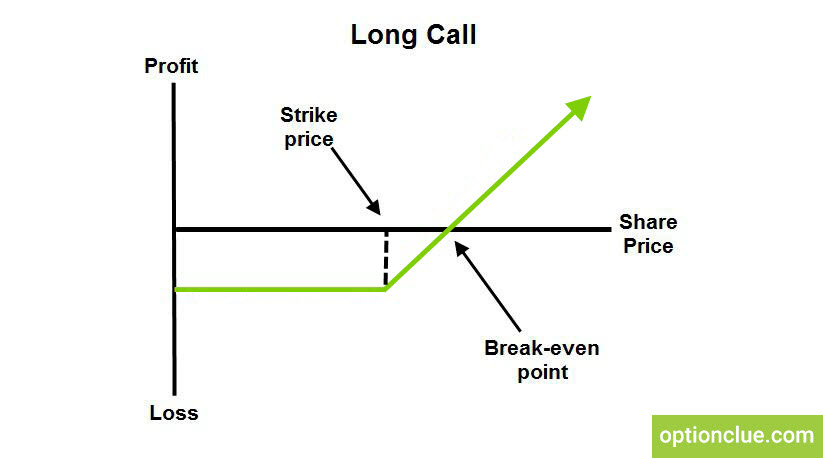
Suppose, we buy the call option for $20. When the strike is $100, the break-even point will be $120 ($100+$20). The call option will be in-the-money when the price is $121 or higher and we will benefit when selling it. We’ll suffer losses if this option is expired at a price below $120.
